Retail
Build high-performance shopping experiences
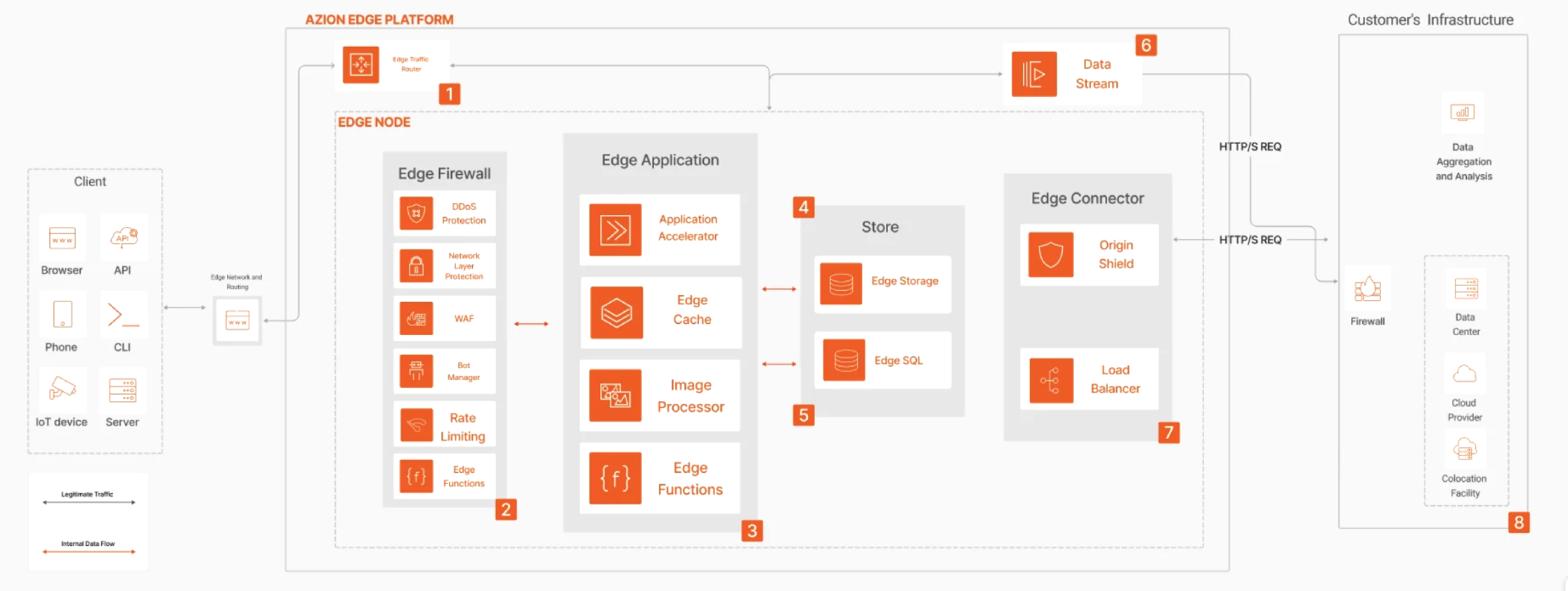
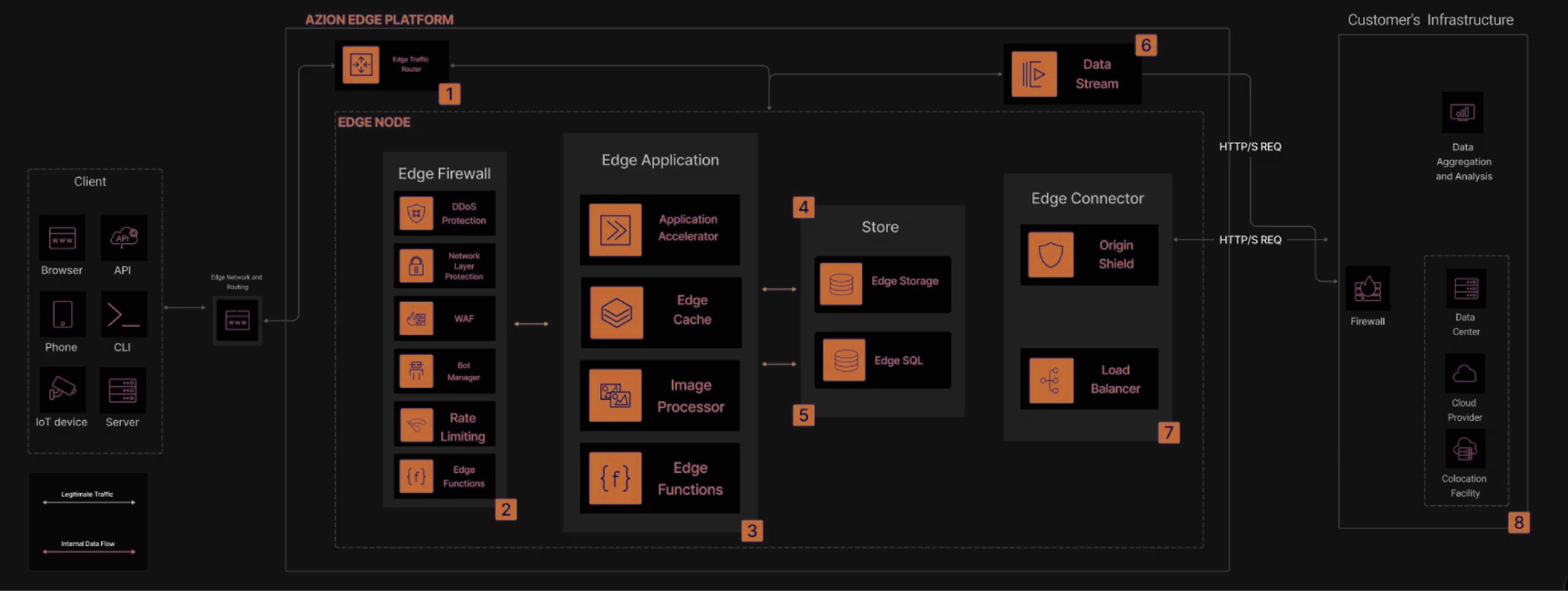
Transform your retail platform with Azion, delivering lightning-fast shopping experiences that maintain performance even during peak events. Our edge security safeguards transactions while preventing fraud, all while reducing infrastructure costs by efficiently handling traffic spikes without overprovisioning—boosting conversions and optimizing your bottom line.
High-performance shopping experience
Build modern retail applications that deliver ultra-fast page loads and optimized transactions, ensuring seamless performance during peak events, improving SEO ranking and driving higher conversion rates.
Enterprise-grade security
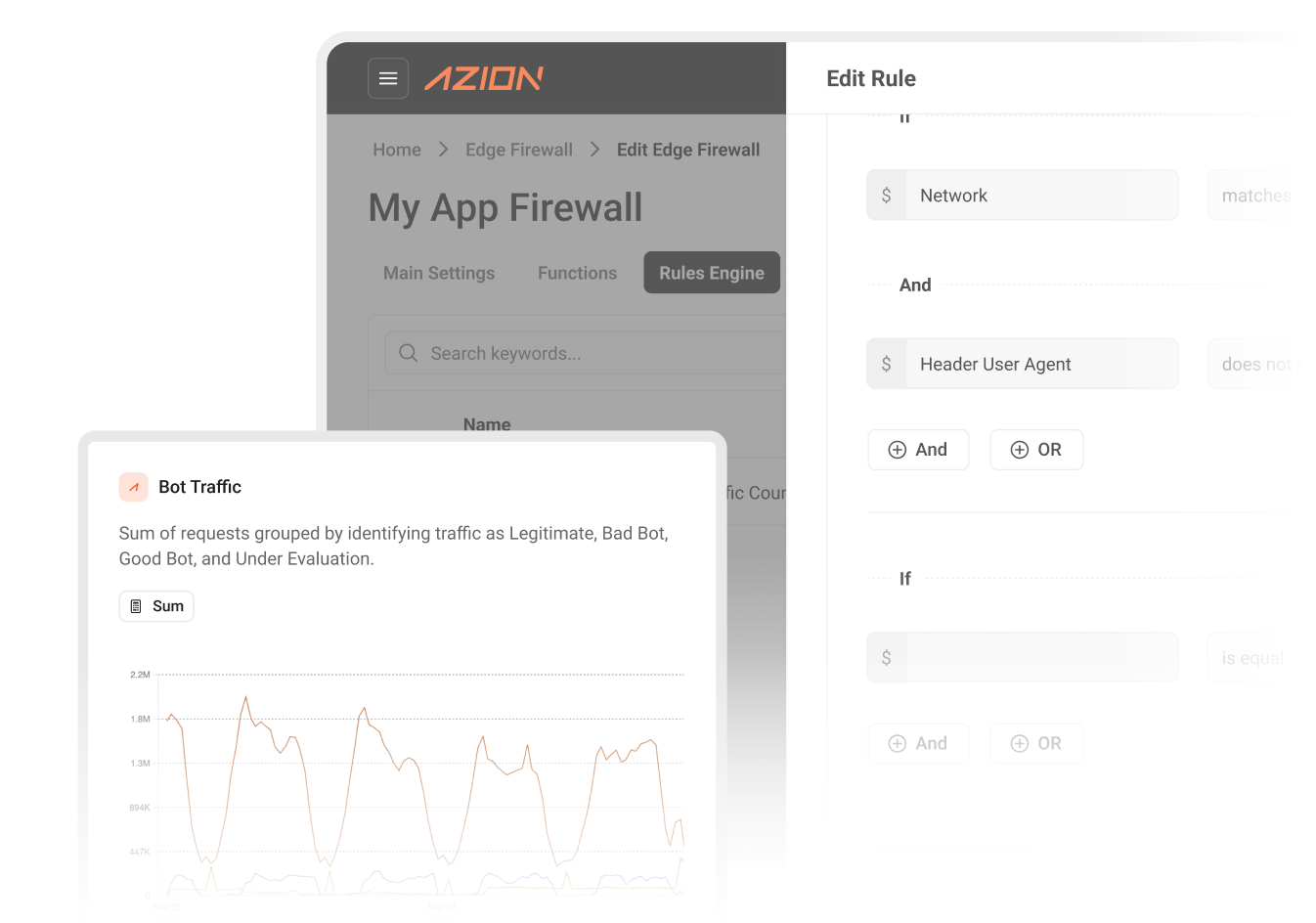
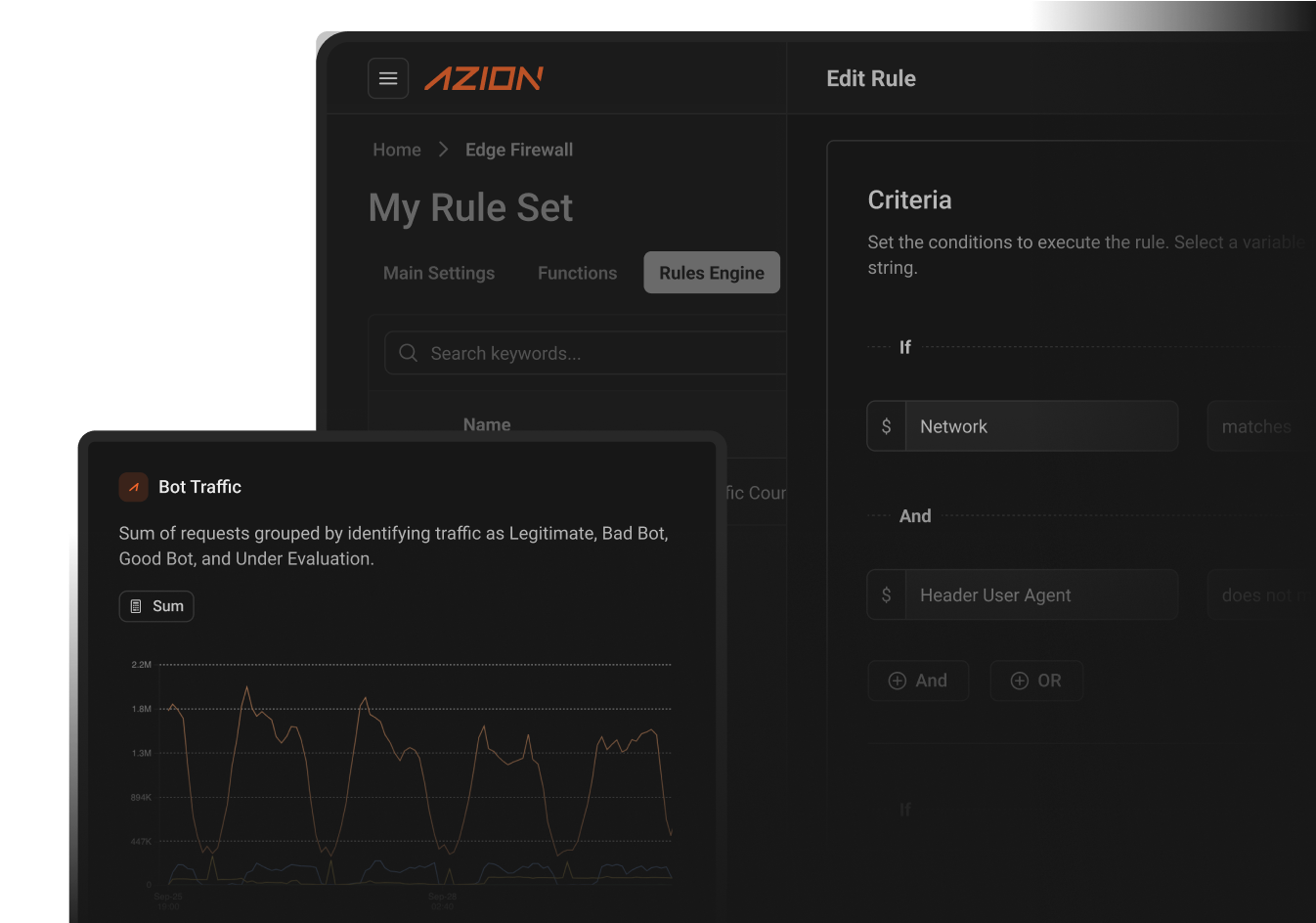
Protect your digital commerce with multi-layered security at the edge, including automated threat detection, fraud prevention, and real-time monitoring while maintaining high availability during critical security events.
Cost reduction
Reduce cloud and infrastructure costs by offloading requests to the edge, optimizing image processing and data transfer, while automatically handling traffic spikes without the complexity of managing servers or overprovisioning resources.
Leading retailers trust Azion
Magalu guarantees high availability for hundreds of global-scale applications with enhanced security perimeter.
View success story
Lojas Renner handles massive traffic spikes and saves 67% on data transfer costs.
View success story
Dafiti achieves 86% faster load times and 45% cost reduction in data transfer.
View success story
Impact at scale
faster page load times compared to legacy solutions
of customer requests served instantly from the edge
average cost reduction in infrastructure and data transfer
Accelerate retail application modernization at the edge
Products and services related to retail edge computing
Trust established through the most rigorous certifications in the market
To ensure customers can use our services with complete confidence, Azion adheres to strict security, availability, and privacy standards.
PCI DSS 4.0
PCI DSS 4.0 certification achieved in 2023, its launch year
SOC 2 Type II
Security and availability for the processing of data close to the end user in the entire Azion network
SOC 3
The SOC 3 report publicly certifies our organizational security
Sign-up and get $300 to use for 12 months.
Access to all products
No credit card required
Credit available to use for 12 months