Introduction
The hyperconnected economy requires higher quality, faster and more consistent user experiences, and this poses increasing challenges for ISPs. With more and more devices connected to the Internet, demand continues to increase exponentially, and it’s necessary to ensure customers are kept happy. However, at the same time, companies must find smart ways to grow without losing control of costs. Building solutions that are focused on improving routing is one of the main challenges in today’s reality. This blog post will provide a closer look at the Azion Edge Network and how Azion’s Edge Traffic Router uses SDN (Software-Defined Networking) to deliver superior performance to our customers.
The Azion Edge Network Basics
At Azion, our main objective is to build a modern, efficient, highly scalable, and secure network with software-based routing. Although BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is the most commonly used protocol to connect public networks around the world, it presents serious operational and security limitations, as we explained in this blog post. Since Azion uses BGP as part of our routing strategy, it was critical that we implement a more modern and programmable approach.
Considering these limitations, Azion decided to use SDN to optimize traffic routing, in conjunction with a more secure distributed network. Our Azion Edge Network is the architecture on which the Azion Web Platform and all our products run. Specifically, our Edge Network was built using software-defined routing, allowing us to get a new level of scalability, flexibility and efficiency while providing all the edge computing intelligence and resources to our customers. To build a network that is modern, efficient and global, we’ve developed a network strategy that includes connectivity, routing and security solutions that guarantee intelligent content delivery and best-in-class services.
Our Edge Network leverages a highly distributed architecture, including edge locations located in strategic places (such as ISPs, last-mile providers and data centers) and connectivity to multiple IXPs (Internet Exchange Points), private and public peerings, and tier 1 transit providers around the world. Delivering from the edge, closer to users, enables lower latency, faster real-time response, improved availability and more fault-tolerance.
And in terms of security, one of the advantages of edge computing is preventing users’ requests from reaching the origin infrastructure, since requests are processed and resolved on the edge of the network. However, this added security is not enough for us. Securing our edge network and our clients’ applications is a priority, and one of our core values is to deliver high service availability without impacting performance. For this, each one of our edge locations has built-in DDoS protection and peering with multiple mitigation centers around the world. Our security suite also includes Network Layer Protection and Web Application Firewall. Additionally, we’ve partnered with many of our competitors and the Internet Society on the MANRS initiative to strengthen Internet routing security.
Finally, Edge Traffic Router is our internal and proprietary routing intelligence that all clients benefit from when using any of our products. If you use Azion, you are using our Edge Network, including our router to solve your requests. Edge Traffic Router is a distributed edge routing service that improves performance, reliability, and costs by extending SDN to the public Internet.
Following the SDN concept, our routing solution is composed of the following elements:
- Global Controller takes care of network traffic, local link routing (intra Edge Locations) and forwarding BGP announcements in a centralized way.
- Edge DNS and BGP Speaker and BGP Controller execute all the tasks related to the routing, such as collecting network data or using such data to answer DNS queries.
- Edge Node resources and network monitoring features collect all the data to feed the controller with the network status in real-time and make the best routing decisions.
How Does Azion’s Edge Traffic Routing Work?
Edge Traffic Router’s main goal is to provide the most efficient routing traffic intelligence to redirect our clients to the best edge location available, taking advantage of Azion’s highly distributed edge network. Determining the optimal network path is one of the main advantages of using SDN, because it allows us to configure which metrics the network needs to check and make decisions dynamically. To do that, Edge Traffic Router is programmed (using SDN capabilities) to determine, using previously defined parameters, the fastest and most efficient path a data package should follow, and to ensure that all data packets are always delivered.
To define the parameters of how requests will be handled, information about the request itself (such as provider, location, device, what is requested, etc.) as well as the conditions of the network nodes (health, availability, resources, proximity, etc.) are taken into account. Then, intelligent rules can be created to define the paths. This way, when a request reaches the network, it completes its journey, as shown below:
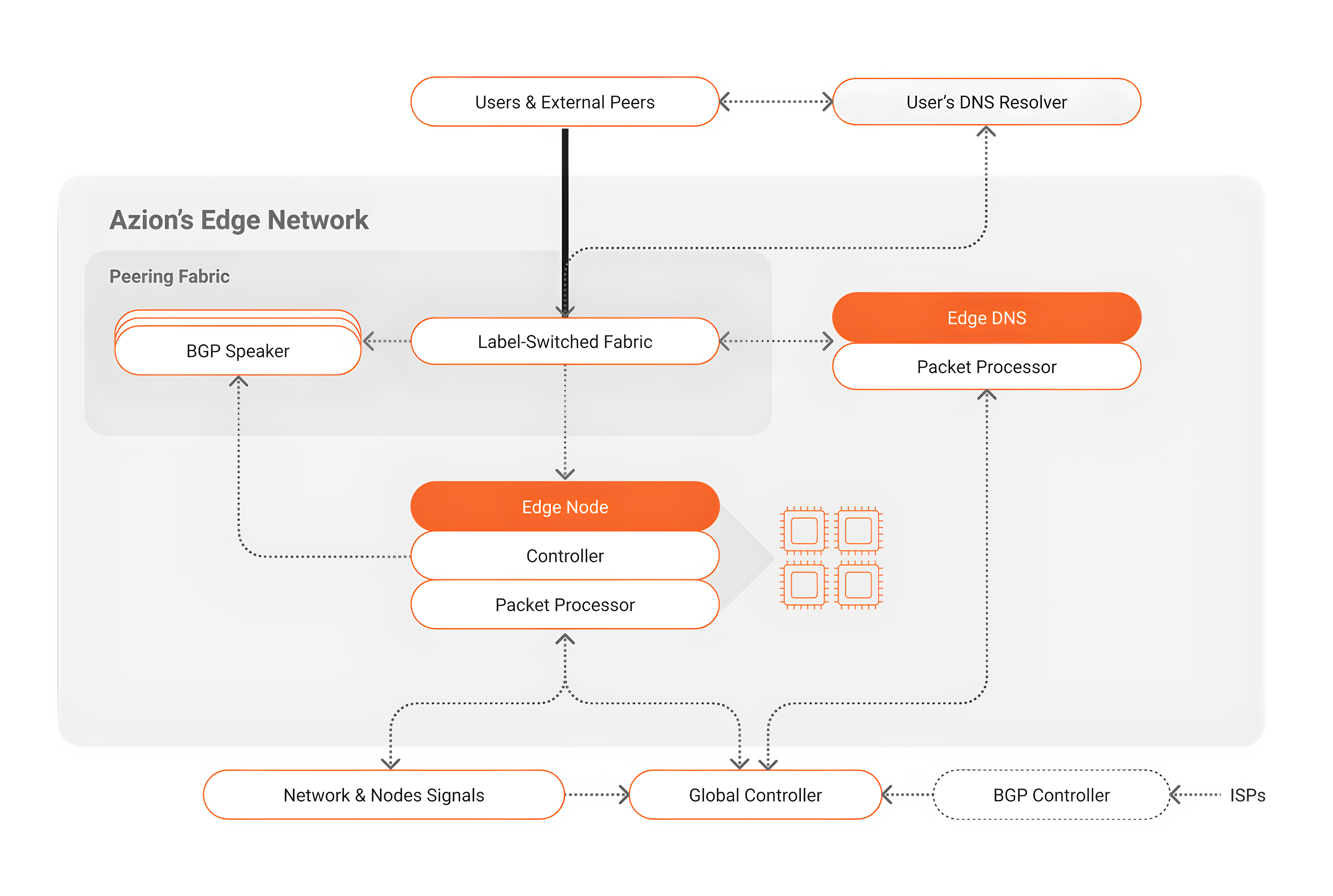
- When the user sends a request, the browser needs to initiate a new HTTP request; first, it must translate the desired domain in the URL to an IP address by using the DNS protocol, then the request can be routed to the most appropriate edge computing server.
- When Azion Edge Network is selected to receive requests from users or external peers, our **Edge DNS ** uses our parameters to verify all the information about the requests to segment and route them efficiently, then it processes the packet and completes a DNS query through the Label-Switched Fabric to determine the next step.
- Since our Edge DNS is able to speak with the Global Controller, it knows what is happening inside each edge node and the status of the network in real-time. Our controller receives data in real-time about parameters such as the availability, health, throughput, and resources (CPU, disk I/O, etc.) of each node (through Edge Node resources and network monitoring features and the BGP Controller, in the case of ISPs connected to our network). This way, the best path is defined in order to guarantee a faster and more efficient response. All the data used in this mission is collected from millions of netflows and nodes every second and Real User Monitoring; our Azion Edge Pulse also helps with this task.
- Besides generating its own status data, our Edge Nodes and Global Controller, which have all the Azion edge intelligence, can also communicate with external ISPs to know their status and announce through the BGP Speaker when necessary to make a hop to an ISP; they are constantly interchanging information to set the policies and parameters to make the connections.
- The user receives the right IP address, which will accept and process the request, and the request comes back to the network through the Label-Switched Fabric.
- Finally, the request is sent to the server or the edge node, and generates a response to the user.
Extending SDN to the Public Internet
Beyond the limitations of BGP, the SDN principles also have some restrictions. SDN was created focused on local area networks (LANs) and private data centers, limiting its possibilities, while SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) connects distributed branches to headquarters through the Internet, rather than via MPLS. However, none of these options, by itself, provides the right solution for connecting a network to the public Internet.
Azion extends SDN to the public Internet using SDN fundamentals (such as separating the control and data plane and centralizing the network control in a global controller) to connect all of Azion’s Edge Network with other networks, ISPs, and telecom providers, among others. And more: being located at the edge also extends the perimeter of the network closer to the users and devices that generate requests and data. This guarantees that when a request is sent to our Edge Network, it’ll be processed in a node that is healthy, available and close to the user, ensuring high availability, ultra-low latency and a faster response time.
SDN principles, combined with widely used standards (such as BGP) and our intelligent edge platform, enable the routing process outside and beyond a private and particular network to be inserted into the public Internet to provide the best path, wherever it leads. Additionally, this more comprehensive approach optimizes the routing process, making the best decision based on real-time data and avoiding overloading any node through techniques like load balancing.
Comparing Azion’s Edge Traffic Router with BGP
As we mentioned in a previous post, BGP has both operational and security issues. BGP is a protocol with a long story, and its launch represented a big evolution, but it’s not prepared for the dynamic needs and flexibility required today. One of the biggest limitations is that BGP is synchronous. This means that when BGP is used, you must have the necessary capacity to deliver and process a specific volume of requests, limiting the possibilities of scale and causing increased latency and network overloads during traffic peaks.
This protocol also does not know the behavior parameters of the network (latency, throughput, availability, etc.), so its decisions are not necessarily the best and it can’t be programmed with intelligent rules or execute dynamic decisions in real-time. There is also the possibility of an incorrect manual peering configuration between ASes or route flapping. Additionally, BGP is not capable of meeting the routing needs of a more complex modern Internet with more and more ASes being connected, and it is usually a slow protocol because route propagation convergence is slow, causing delays, packet loss, and limited access for users.
Finally, BGP is not secure, so it’s vulnerable to increasingly frequent threats, such as BGP manipulation (where routing is modified by a hacker), DDoS attacks (where hackers send a large amount of data or requests to reduce the computational resources for processing legitimate traffic) and BGP hijacking (where hackers redirect Internet traffic to unwanted sites, falsely advertising ownership of a victim’s IP address).
But even with all the limitations, BGP still plays an important role in Internet traffic routing when used as part of more comprehensive strategies that mix different protocols and approaches in order to ensure the best choice to solve requests. There are different benefits of using an edge platform like Azion’s, and building a robust strategy for routing and networking, including the use of SDN and BGP together, helps us to boost these benefits and deliver the best performance, availability, and resiliency to our customers:
- by allowing you to reach any place around the world in milliseconds through our highly distributed network with more than 100 edge locations, and connected to another AS or network in the public Internet;
- by avoiding overloading a node and preventing any singular failure from affecting the service entirely;
- by processing data closer to the source and prioritizing traffic distribution, reducing the distance data needs to travel, and avoiding unnecessary requests to the cloud or origin infrastructure;
- by intelligently choosing the best network path to resolve requests using less bandwidth and reducing response time, and providing the capacity to respond quickly to any incident or traffic peak;
- by providing real-time data to monitor the behavior and functionality of the network through our suite of specialized products;
- by reducing operational costs and developer efforts through the creation of rules that define network behaviors; and
- by detecting and repealing any threats on the edge, avoiding damage to the origin infrastructure.
Do you want to test our full suite of products? You can create a free account and get $300 in credit or contact our experts to start your digital transformation journey and move to the edge!
At Azion, we are hiring now! If you want to work with these technologies and build the future of computing with us, check all the vacant positions in our Careers section.







